1、widthStep定义:①OpenCV中,默认图闻赙酵枭像原点为图像左上角,img->origin=IPL_ORIGIN_TL;如果想更改图像原点坐标也可以,如img->origin=IP讣嘬铮篌L_ORIGIN_BL,将图像原点更改为左下角;一般采用默认的图像原点;②OpenCV用imread或者cvLoadImage得到的图像数据都是unsigned char类型的;③IplImage结构体中的widthStep元素大小不一定等于width*nChannels,④在cxcore/cxarray.cpp文件中,cvInitImageHeader对widthStep大小赋值:image->widthStep =(((image->width * image->nChannels *(image->depth & ~IPL_DEPTH_SIGN) + 7)/8)+ align - 1) & (~(align - 1)); 其中,cxtypes.h定义IPL_DEPTH_SIGN为:#define IPL_DEPTH_SIGN 0x80000000;cxmisc.h中定义align为:#define CV_DEFAULT_IMAGE_ROW_ALIGN 4;depth取8位深度;则可计算图像的widthStep;一些图像的widthStep如下:IplImage *image_33 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(3, 3), 8, 3);IplImage *image_31 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(3, 3), 8, 1);IplImage *image_53 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(5, 3), 8, 3);IplImage *image_51= cvCreateImage(cvSize(5, 3), 8, 1);IplImage *image_73 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(7, 3), 8, 3);IplImage *image_71 = cvCreateImage(cvSize(7, 3), 8, 1);printf("%d, %d, %d, %d, %d, %d",image_33->widthStep,image_31->widthStep,image_53->widthStep,image_51->widthStep,image_73->widthStep,image_71->widthStep);运行结果为:12, 4, 16, 8, 24, 8。因此,OpenCV分配的内存按4字节对齐,与上述计算结果相符,如宽度为3、通道数为3的图像,每一行需要的实际内存长度为3*3,为了内存对齐,OpenCV会在每行末尾自动补上3个字节的内存,内存初始化都为0,所以widthStep变为了12。
2、widthStep在IplImage*中的作用:如下:typedef struct _IplImage{ int nSize; /* sizeof(IplImage) */ int ID; /* version (=0)*/ int nChannels; /* Most of OpenCV functions support 1,2,3 or 4 channels */ int alphaChannel; /* Ignored by OpenCV */ int depth; /* Pixel depth in bits: IPL_DEPTH_8U, IPL_DEPTH_8S, IPL_DEPTH_16S, IPL_DEPTH_32S, IPL_DEPTH_32F and IPL_DEPTH_64F are supported. */ char colorModel[4]; /* Ignored by OpenCV */ char channelSeq[4]; /* ditto */ int dataOrder; /* 0 - interleaved color channels, 1 - separate color channels. cvCreateImage can only create interleaved images */ int origin; /* 0 - top-left origin, 1 - bottom-left origin (Windows bitmaps style). */ int align; /* Alignment of image rows (4 or 8). OpenCV ignores it and uses widthStep instead. */ int width; /* Image width in pixels. */ int height; /* Image height in pixels. */ struct _IplROI *roi; /* Image ROI. If NULL, the whole image is selected. */ struct _IplImage *maskROI; /* Must be NULL. */ void *imageId; /* " " */ struct _IplTileInfo *tileInfo; /* " " */ int imageSize; /* Image data size in bytes (==image->height*image->widthStep in case of interleaved data)*/ char *imageData; /* Pointer to aligned image data. */ int widthStep; /* Size of aligned image row in bytes. */ int BorderMode[4]; /* Ignored by OpenCV. */ int BorderConst[4]; /* Ditto. */ char *imageDataOrigin; /* Pointer to very origin of image data (not necessarily aligned) - needed for correct deallocation */}IplImage;
3、IplImage*访问图像像素:widthStep对呖分甾胗8bit,单通道,unsigned char类型的图像I---朐袁噙岿IplImage* img:I(x, y)~((unsigned char*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x];对8bit,3通道,unsigned char类型的图像I---IplImage* img:I(x, y)blue~((unsigned char*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x*3];I(x, y)green~((unsigned char*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x*3+1];I(x, y)red~((unsigned char*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x*3+2];或者unsigned char* ptr=&((unsigned char*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x*3];I(x, y)blue ~ ptr[0];I(x, y)green~ ptr[1];I(x, y)red ~ ptr[2];对32bit,1通道,float*类型的图像I---IplImage* img:I(x, y)~((float*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x];对32bit,3通道,float*类型的图像I---IplImage*img;I(x, y) blue ~((float*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[3*x];I(x, y) green ~(( float *)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x*3+1];I(x, y) red ~(( float *)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x*3+2];对64bit,3通道,double*类型的图像数据I--- IplImage*img;image=cvCreateImage(cvSize(111,113),IPL_DEPTH_64F,3);这里widthstep=(111*3*sizeof(double)+3)/4*4=2664;因为111*3*sizeof(double)=2664已经正好是4的倍数了,因此无需补充字节。如果用指针访问第31行、51列的图像数据,则这个数据为double类型的,image->imageData为unsigned char类型,因此可以转换成double,通过double指针来访问:①double *data=(double*)image->imageData;double val=*(data+31*width+51);②或者通过unsigned char指针找到(31,51)处的地址,然后转换成double指针进行访问:unsigned char* data=image->imageData;double val=*(double*)(data+31*image->widthStep+51*sizeof(double)); 对于IplImage,指针访问可以参考以上两种方式,其实这本质就是数据类型的转换而已。一般,访问图像像素方法,格式:对于N通道,T类型的图像,I(x,y)c~((T*)(img->imageData+img->widthStep*y))[x*N+c];
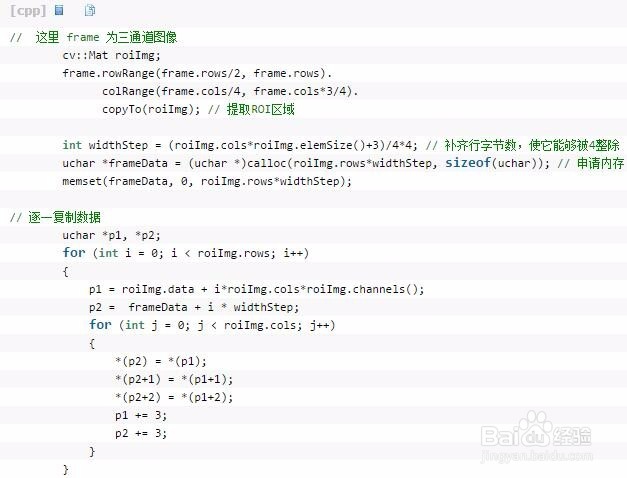
4、widthStep知识总结:width表示图像的每行像素数,widthStep表示存储一行像素需要的字节数,widthStep必须是4的倍数,从而实现字节对齐,有利于提高运算速度。如果8U单通道图像宽度为3,那么widthStep是4,加一个字节补齐。这个图像的一行需要4个字节,只使用前3个,最后一个空着。也就是一个宽3高3的图像的imageData数据大小为4*3=12字节。【注】:不同数据类型长度的图像,widthStep也不相同;widthStep的值的计算有两种情况:①当(width*3)%4=0,这时width*3=widthStep;②当(width*3)%4 !=0,此时widthStep=(width/4+1)*3。Mat的数据并不是字节对齐的;直接将cv::Mat转换为IplImage类型,并不会将字节对齐,只是加了个文件头而已;因此需要如下操作:
5、BYTE*与IplImage*之间的转换:IplImage* iplImage:opencv中图像数据头;BYTE* data:内存中的图像数据,一般为工业相机采集的图像数据;①由IplImage*转BYTE*图像数据:data = iplImage->imageDataOrigin; //未对齐的原始图像数据或者data = iplImage->imageData; //已对齐的图像数据②BYTE*转IplImage*图像数据iplImage = cvCreateImageHeader(cvSize(width,height),depth,channels);cvSetData(iplImage,data,step);首先,由cvCreateImageHeader()创建IplImage图像头,设置图像尺寸、深度和通道数;然后,由cvSetData()根据BYTE*图像数据指针设置IplImage图像头的数据,其中,step指定该IplImage图像,每行占的字节数,对于1通道的 IPL_DEPTH_8U图像,step可以等于width。
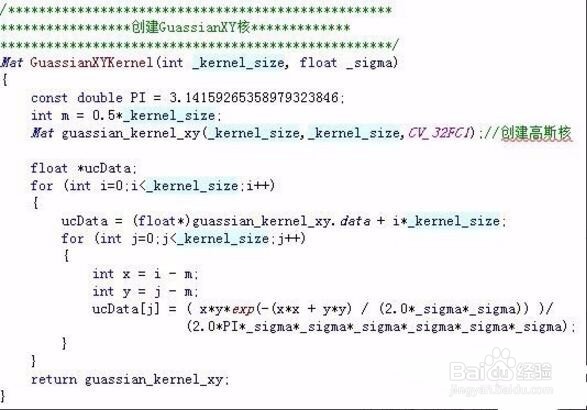
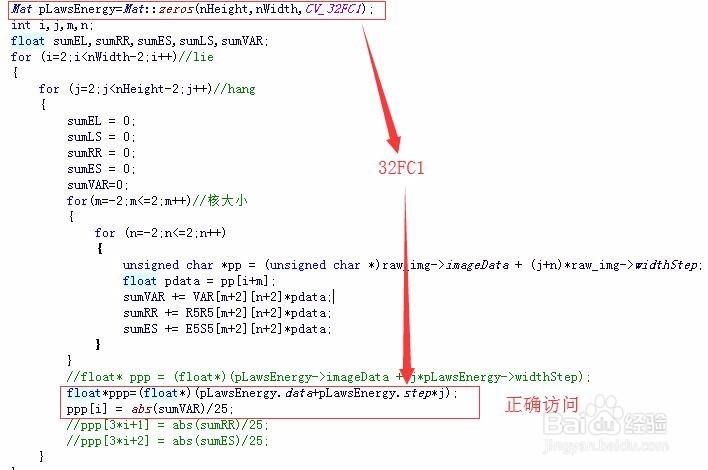
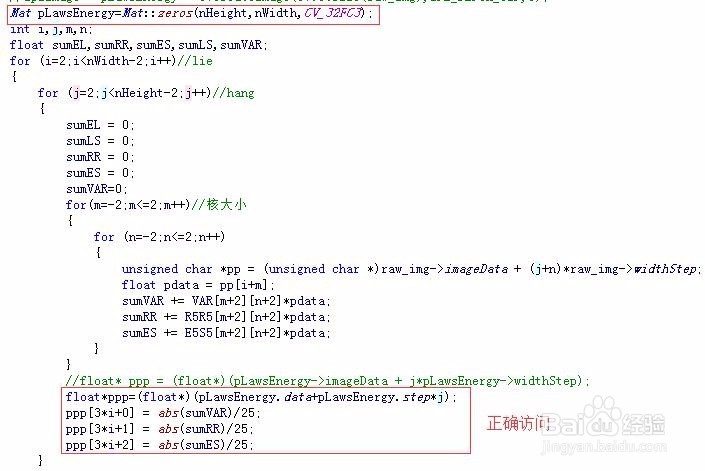
6、Mat访问图像像素---step:data:unsigned char类型的指针,指向Mat数据矩阵的首地址;dims:Mat矩阵的维度;rows:Mat矩阵的行数;cols:Mat矩阵的列数;size():是一个结构体,有image.size().width==image.cols; image.size().height==image.rowschannels():Mat矩阵元素拥有的通道数;depth:度量每一个像素中每一个通道的精度,但它本身与图像的通道数无关!depth数值越大,精度越高。在Opencv中,Mat.depth()得到的是一个0~6的数字,分别代表不同的位数,如下:{CV_8U=0,CV_8S=1,CV_16U=2,CV_16S=3,CV_32S=4,CV_32F=5,CV_64F=6}elemSize:表示矩阵中每一个元素的数据大小,单位字节,如果Mat中的数据类型是CV_8UC1,那么elemSize==1;如果是CV_8UC3或CV_8SC3,那么elemSize==3;如果是CV_16UC3或者CV_16SC3,那么elemSize==6;即elemSize是以8位(一个字节)为一个单位,乘以通道数和8位的整数倍;elemSize1:表示Mat矩阵中每一个元素单个通道的数据大小,单位字节,elemSize1=elemSize/channels;step:为Mat矩阵中每一行的“步长”,以字节为基本单位,每一行中所有元素的字节总量;step1():以字节为基本单位,Mat矩阵中每一个像素的大小step1==step/elemSize1;type:Mat矩阵的类型,包含有矩阵中元素的类型、通道数信息,type的命名格式为CV_(位数)+(数据类型)+(通道数),如下:
7、Mat访问图像像素---stepstep:为Mat矩阵中每一行的“步长”,以字节为基本单位,每一行中所有元素的字节总量;经常应用在访问图像像素操作中;如下:对8bit,单通道,unsigned char类型的图像I---Mat img:unsigned char* pData=(unsigned char*)img.data;I(x, y)~pData[img.step*y+x];//对8bit,3通道,unsigned char类型的图像I---IplImage* img:I(x, y)blue~((unsigned char*)(img.data+img.step*y))[x*3];I(x, y)green~((unsigned char*)(img.data+img.step*y))[x*3+1];I(x, y)red~((unsigned char*)(img.data+img.step*y))[x*3+2];对32bit,1通道,float*类型的图像I---Mat img:I(x, y)~((float*)(img.data+img.step*y)[x];对32bit,3通道,float*类型的图像I--- Mat img;I(x, y) blue ~((float*)(img.data+img.step*y))[3*x];I(x, y) green ~((float*)(img.data+img.step*y))[x*3+1];I(x, y) red ~((float*)(img.data+img.step*y) )[x*3+2];对64bit,1通道,double*类型的图像I---Mat img:I(x, y)~((double*)(img.data+img.step*y)[x];对64bit,3通道,double*类型的图像数据I--- Mat img;I(x, y) blue ~(( double *)(img.data+img.step*y))[3*x];I(x, y) green ~(( double *)(img.data+img.step*y))[x*3+1];I(x, y) red ~(( double *)(img.data+img.step*y))[x*3+2];一般,访问图像像素方法,格式:对于N通道,T类型的图像,I(x,y)c~((T*)(img.Data+img.step *y))[x*N+c];