1、1)Isotropic Elastic Model(各项同性材料):DENS(密度)、EX(弹性模量)、NUXY(泊松比),各向同性材料高碳钢的材料属性如下:
2、2)Orthotropic Elastic Model(正交各项异性材料):DENS(密度)弹模:EX(X向弹性模量)、EY(Y向弹性袷蜍滇刷模量)、EZ(Z向弹性模量)泊松比,需要定义一组最小泊松比或者一组主方向泊松比:Minor Poisson's ratio:NUXY(XY方向泊松比)、NUYZ(YZ方向泊松比)、NUXZ(XZ方向泊松比)或者-MajorPoisson's ratio:PRXY(XY方向泊松比)、PRYZ(YZ方向泊松比)、PRXZ(XZ方向泊松比)剪模:GXY(XY剪模量)、GXZ(XZ剪模量)、GYZ(YZ剪模量)举例矾土(氧化铝)各向异性材料如下:
3、3)Anisotropic Elastic Model(各向同性材料):This material description requires the full elasticity matrix. Because of symmetry, only 21 constants are required. This material is only valid for SOLID164 and SOLID168 elements,for exampleCadmium:
4、4)Elastic Fluid Model(弹性流体材料):DENS(密度)、体积弹性模量,可以通过EDMP,FLUID,MAT,VAL1;直接定义体积弹性模量或者通过定义流体的弹性模量和泊松比,程序自行计算,公式如下:
5、5)Blatz-Ko Rubber Elastic Model(Blatz-Ko 橡胶弹性模型):这种超弹性模型,只需要定义材料的密度DENS、剪切弹性模量GXY:
6、6)Bilinear Isotropic Model(双线性各向同性模型):Classical biline锾攒揉敫ar isotropic hardening model (strain rate independent) that uses two slopes (elastic and plastic) to represent the stress-strain behavior of a material. Specify the stress-strain behavior at only one temperature. 除了在MP模块施加密度、弹性模量、泊松比以外,需要在TBDATA板块施加Yield stress(屈服应力)、tangent modulus(切线模量),例如镍合金材料:
7、7)Temperature Dependent Bilinear Isotropic Model(基于温度的双线性各向同性模型):For this material model, you must supply data over a temperature range wide enough to cover the actual temperatures that will occur in the analysis. Otherwise, the analysis will terminate.
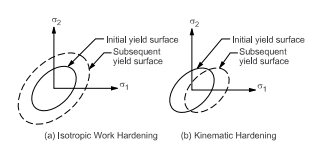
8、8)Bilinear Kinematic Model(双线性随动模型):与各项同性模型类似,只不过随动强化方式与各向同性强化方式有区别,如下:
9、9)Plastic Kinematic Model(塑性随动模型):Isotropic and kinematic contributions may be varied by adjusting the hardening parameter β between 0 (kinematic hardening only) and 1 (isotropic hardening only),1018钢材料的具体示例如下:
10、10)Piecewise Linear Plasticity Model(分段线性塑性模型):其需要输入的参数以及高碳钢材料的分段线性塑性模型,如下: